
![]()
- Definition and Overview of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Physical Causes of ED
- Psychological and Emotional Factors Affecting ED
- Prevalence: The 30 Million Men Affected
- Identifying ED: The 25% Frequency Benchmark
- Treatment Options for ED
- Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Approach
- The Importance of Consulting a Doctor for ED
- Orgasm, Ejaculation, and Erection: The Distinctions
Definition and Overview of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction, often abbreviated as ED, is a condition where an individual struggles to obtain or sustain an erection that's adequate for sexual activities. While ED is common, especially with increasing age, it's not a straightforward diagnosis. It can be symptomatic of other underlying health problems or could be exacerbated by emotional disturbances.
Physical Causes of ED
Various medical conditions can contribute significantly to erectile dysfunction. Conditions like heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, and notably diabetes, have been linked to ED. For instance, over 50% of men with diabetes experience ED. Other conditions like multiple sclerosis and kidney disease also play a role in the development or exacerbation of ED.
Psychological and Emotional Factors Affecting ED
Beyond the physical aspects, ED is often associated or worsened by emotional problems. Mental health issues like depression, anxieties, stress, and relationship problems can severely interfere with sexual feelings. These can hamper one's ability to achieve or maintain an erection, even in the absence of any physical ailments.
Prevalence: The 30 Million Men Affected
It's crucial to understand that ED isn't an isolated problem.
It affects millions worldwide.
Its prevalence underscores the need for accurate diagnosis and effective treatments, emphasizing that those affected are not alone.
Identifying ED: The 25% Frequency Benchmark
One can characterize ED by its frequency. If someone struggles to maintain an erection over 25% of the time, it could be a sign of erectile dysfunction. However, ED is when one regularly cannot achieve and maintain an erection. This condition might be specific to certain situations or could be a consistent issue.
Treatment Options for ED
Depending on the root cause, ED treatments can vary. For those with psychological triggers, counseling and therapy prove beneficial. For physical causes, medications and surgeries can be effective options. Before opting for any treatment, it's crucial to discuss with a healthcare professional and understand the possible risks and benefits.
Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Approach
![]() A healthy lifestyle can have a significant positive impact on sexual health. Adopting healthier habits such as eating well, regular exercising, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, ensuring adequate sleep, open communication with a partner, and managing stress are pivotal. These can enhance one's sexual responsiveness and potentially mitigate the symptoms of ED.
A healthy lifestyle can have a significant positive impact on sexual health. Adopting healthier habits such as eating well, regular exercising, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, ensuring adequate sleep, open communication with a partner, and managing stress are pivotal. These can enhance one's sexual responsiveness and potentially mitigate the symptoms of ED.
The Importance of Consulting a Doctor for ED
While understanding and self-education about ED are important, it's paramount to consult with a doctor. A healthcare professional can provide accurate diagnosis, inform about potential underlying conditions, and recommend effective treatments tailored to individual needs.
Orgasm, Ejaculation, and Erection: The Distinctions
Interestingly, an erection isn't a prerequisite for orgasm or ejaculation. Men with ED can still experience both orgasm and ejaculation without a full erection. In some cases, even if a man can't maintain a firm erection, other forms of sexual stimulation can lead to an orgasm, ensuring both partners enjoy sexual pleasure.
So, in response to the question, "Can erectile dysfunction make you hard?": Yes, people with ED can still achieve an erection and even orgasm, but the frequency and consistency might be affected. The combination of physical and emotional factors plays a complex role in this, but with the right approach and treatment, one can manage and potentially overcome the challenges posed by ED.
- how to stop headache with viagra?
- where can i buy non prescription viagra
- what is the use for sildenafil 20 mg tablets?
- new medicine for erectile dysfunction
- why do i get performance anxiety in bed?
- is ed caused by clogged arteries?
- what causes blue vision with viagra?
- is there a daily viagra?
- does viagra cure impotence?
- does norvasc cause erectile dysfunction?
- who holds the patent for viagra and when did pfizer lose it?
- can you take flomax and cialis together?
- can tramadol help a man last longer in bed?
- is there a safe herbal viagra?
- how long does 20mg viagra last?
- does cialis work after prostate removal?
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Definition and Overview of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Physical Causes of ED
- Psychological and Emotional Factors Affecting ED
- Prevalence: The 30 Million Men Affected
- Identifying ED: The 25% Frequency Benchmark
- Treatment Options for ED
- Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Approach
- The Importance of Consulting a Doctor for ED
- Orgasm, Ejaculation, and Erection: The Distinctions
Definition and Overview of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction, often abbreviated as ED, is a condition where an individual struggles to obtain or sustain an erection that's adequate for sexual activities. While ED is common, especially with increasing age, it's not a straightforward diagnosis. It can be symptomatic of other underlying health problems or could be exacerbated by emotional disturbances.
Physical Causes of ED
Various medical conditions can contribute significantly to erectile dysfunction. Conditions like heart disease, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, and notably diabetes, have been linked to ED. For instance, over 50% of men with diabetes experience ED. Other conditions like multiple sclerosis and kidney disease also play a role in the development or exacerbation of ED.
Psychological and Emotional Factors Affecting ED
Beyond the physical aspects, ED is often associated or worsened by emotional problems. Mental health issues like depression, anxieties, stress, and relationship problems can severely interfere with sexual feelings. These can hamper one's ability to achieve or maintain an erection, even in the absence of any physical ailments.
Prevalence: The 30 Million Men Affected
It's crucial to understand that ED isn't an isolated problem.
It affects millions worldwide.
Its prevalence underscores the need for accurate diagnosis and effective treatments, emphasizing that those affected are not alone.
Identifying ED: The 25% Frequency Benchmark
One can characterize ED by its frequency. If someone struggles to maintain an erection over 25% of the time, it could be a sign of erectile dysfunction. However, ED is when one regularly cannot achieve and maintain an erection. This condition might be specific to certain situations or could be a consistent issue.
Treatment Options for ED
Depending on the root cause, ED treatments can vary. For those with psychological triggers, counseling and therapy prove beneficial. For physical causes, medications and surgeries can be effective options. Before opting for any treatment, it's crucial to discuss with a healthcare professional and understand the possible risks and benefits.
Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Approach
A healthy lifestyle can have a significant positive impact on sexual health. Adopting healthier habits such as eating well, regular exercising, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, ensuring adequate sleep, open communication with a partner, and managing stress are pivotal. These can enhance one's sexual responsiveness and potentially mitigate the symptoms of ED.
The Importance of Consulting a Doctor for ED
While understanding and self-education about ED are important, it's paramount to consult with a doctor. A healthcare professional can provide accurate diagnosis, inform about potential underlying conditions, and recommend effective treatments tailored to individual needs.
Orgasm, Ejaculation, and Erection: The Distinctions
Interestingly, an erection isn't a prerequisite for orgasm or ejaculation. Men with ED can still experience both orgasm and ejaculation without a full erection. In some cases, even if a man can't maintain a firm erection, other forms of sexual stimulation can lead to an orgasm, ensuring both partners enjoy sexual pleasure.
So, in response to the question, "Can erectile dysfunction make you hard?": Yes, people with ED can still achieve an erection and even orgasm, but the frequency and consistency might be affected. The combination of physical and emotional factors plays a complex role in this, but with the right approach and treatment, one can manage and potentially overcome the challenges posed by ED.
- how to stop headache with viagra?
- where can i buy non prescription viagra
- what is the use for sildenafil 20 mg tablets?
- new medicine for erectile dysfunction
- why do i get performance anxiety in bed?
- is ed caused by clogged arteries?
- what causes blue vision with viagra?
- is there a daily viagra?
- does viagra cure impotence?
- does norvasc cause erectile dysfunction?
- who holds the patent for viagra and when did pfizer lose it?
- can you take flomax and cialis together?
- can tramadol help a man last longer in bed?
- is there a safe herbal viagra?
- how long does 20mg viagra last?
- does cialis work after prostate removal?
- Erectile Dysfunction
|
About GreenLight: For men with bladder outflow obstruction due to an enlarged prostate, this technique allows genuine day case surgery with dramatic early results and minimal early side-effects. Most men can now be treated without a post-operative catheter. It is possible for prostates of all sizes to be treated. Even patients with retention of urine can go home the same day, sometimes with no catheter. Bleeding and recovery time are usually minimal. As the first team in the UK to use the GreenLight system, and having pioneered and developed the GreenLight prostate vaporisation system in Europe, we have now virtually given up other surgical methods of benign prostate surgery. GreenLight Patient Information How does it work? Information for GP's Training Courses for Surgeons
| |
|
Watch patient information video |
By clicking on the flash image you will be able to watch a video where patients share their experiences and an explanation is given of the techniques. You will need to have Flash player installed to watch it. To download our operation information (Adobe PDF) click here
If you prefer to read the information online then click here to go to our operation info page |
|
NHS Innovation Awards The adoption of this technique led to the NHS clinical excellence award for innovation being awarded to King's College Hospital.
| |
How does it work?
Although we had in TURP a very good and tested operation, there are side effects and costs associated with it. This led to many minimally invasive approaches over the last decade. Sadly most of these were abandoned due to or a high risk of pain or other side effects compared to TURP, or because they simply did not work!
Previous Attempts with Lasers
Many laser energies have been used in the prostate before now, but limitations on laser power have meant removal of significant amounts of prostate tissue (the real test) has been impossible or unfeasibly slow. The only two contenders for the TURP crown up until now have been prostate electrovaporisation (easy to learn but higher risk of infection, impotence and incontinence) and holmium laser prostate enucleation (as effective as TURP but extremely difficult to learn and associated with severe operative complications in all but the most expert hands).
The Greenlight HPS system from AMS addresses this problem by means of delivering a very powerful modulated laser beam which is absorbed by the haemoglobin pigment in tissue. This means that when the laser is applied to prostate tissue massive localised heating of the tissue occurs resulting in instantaneous vaporisation: due to the laser - characteristically bleeding is close to zero.
Our results show that prostates of any size can be treated, with most men seeing their symptoms improve by two or three fold in the first six weeks. Many men have continuing benefits developing up to nine months after surgery
The technique allowsrapid creation of a generous prostate cavity with almost no bleeding. More than 50% of men can leave hospital on the day of surgery without a catheter, with most others having a soft small catheter for around 18 hours at home (many men remove this themselves)Althoughwe placed catheters post operatively in our initial evaluation period, only a few men have had to have a catheter for more than 12 hours (these have usually been in urinary retention patients, and nearly all have voided extremely well on final catheter removal. Strikingly, very few patients report pain after the procedure: pain and burning on urinating have limited both laser techniques and TURP in the past. About one man in ten will get some burning which may need a fe weeks of simple painkillers to ease the discomfort. Sexual side effects are reduced compared to the standard technique. While very long term results are awaited, the figures after five years of follow up show improvements in symptoms and urological measurements comparable to historical TURP data (about one man in fifty requiring reintervention each year). In particular it appears the prostate tissue removal seen at the time of surgery is genuine when assessed by post-operative prostate ultrasound (between 40-60% of tissue reduction is seen).
Post operative bleeding and discomfort can occur, but aremuch less than with standard TURP, and many men have gone back to work or normal activities within a couple of days, with sport and other activities being possible within a week or two. Of course, some men do take longer to recover and those men with very overactive bladders or catheters pre-operatlively may take some time to settle afterwards.
Anticoagulation, large prostate size (>100g) and poor cardiac status are not contraindications to the procedure, even as a day case.
Our results have been presented at a number of international meetings including the European Association of Urology and the American Urological Association Meeting. In particular our data on large prostates and the absence of absorption of irrigating fluid has attracted much interest. Mr Muir isa founder member of the International GreenLIght Users' Group, which seeks to fine tune and improve further the results from this therapy.
IPSS Symptom scores changes following PVP to one year
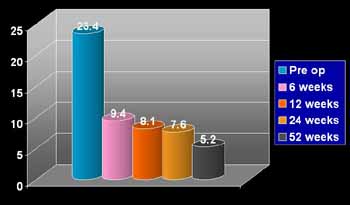
The initial score of 23 on the IPSS system shows that most men were suffering severe symptoms which reduced by almost threefold within sixweeks.
Urine flow rates at the same stage and out to five years in our series showimprovements of more than 100%.
GreenLight Training Courses at King's College Hospital
(for urological surgeons wishing to learn the technique)
Course director: Gordon Muir, Consultant Urologist
The course will be in the format of small group teaching with a mixture of didactic presentations linked to live 2 way videoconferencing observing a number of prostate vaporisations in the operating theatre downstairs from our conference room.. There will be an opportunity to visit our state of the art integrated operating theatres during procedures to observe the set-up and logistical issues relating to prostate laser surgery.
The objectives of the course will be that at the end of the course participants will be able to:
-
Understand the indications and contraindications for GreenLight PVP
-
Explain the mechanism of action and efficacy of high power KTP-YAG laser energy
-
Control an operating theatre with a GreenLight laser installation
-
Apply their understanding of the GreenLight PVP procedure to their clinical practice
Topics covered in the course include:
GreenLight PVP results
Previous lasers: problems and successes
Why green light? Laser physics and safety
Live cases
Theatre and nursing issues
Discussion: how to startup, avoiding complications
Certificates of GreenLight laser training and CME credits will be awarded to those who have successfully completed the training course. CME accreditation has been applied for.
Refreshments and lunch are included in the course fee
Course dates at King's College Hospital
6th April 2009
11th May 2009
8th June 2009
6th July 2009
Training video (NB this is NOT a substitute for attending a properly run course and having mentoring for the surgical technique)
for further information on courses contact [email protected]

Copyright (c) 1999-2001 GH Muir. All rights reserved.
[email protected]
